|
Fig. 1 Cataract Canyon, Green river, Utah. HOW TO CALCULATE ONLINE SEDIMENT DISCHARGE BY THE COLBY METHOD?
Professor Emeritus of Civil and Environmental Engineering
San Diego State University, San Diego,
California
1. INTRODUCTION
Knowledge of sediment transport discharge and concentration
is a requirement in the design of hydraulic conveyance structures. Applications are in
flood control and associated hydraulic structures. Currently, there are quite a few methods available
for the calculation of sediment discharge; however, none are so convenient, straight forward, and predictable
as the Colby 1964 method
2. THE COLBY METHOD
The Colby (1964) method for the calculation of sediment discharge, herein referred to simply as the "Colby method,"
is a methodology to calculate the discharge of sands.
The method is based on Colby's earlier
work (Colby and Hembree, 1955;
Colby, 1957; Ponce, 2014b).
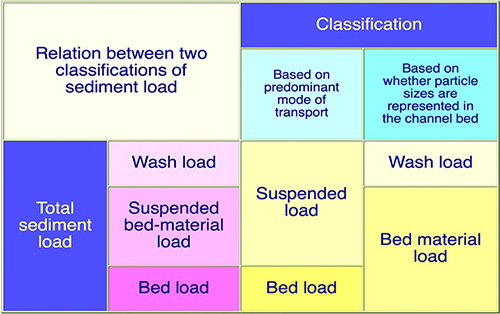
It relies heavily on the relationship between sediment discharge
and mean velocity,
with flow depth and channel width as additional parameters. Secondary parameters are water temperature, bed material size, and wash load concentration (Fig. 2).
3. USE OF THE ONLINE CALCULATOR
The online calculator ONLINECOLBY
was developed in 2020 at the Visualab, Department of Civil, Construction, and Environmental
Engineering, San Diego State University, San Diego,
California.
Output from the calculator
is shown below. The discharge of sands, or sediment discharge, is:

REFERENCES
Colby, B. R., and C. H. Hembree. 1955. Computations of Total Sediment
Discharge, Niobrara River Near Cody, Nebraska. U.S. Geological Survey Water-Supply Paper 1357, Washington, D.C.
https://ponce.sdsu.edu/colby_and_hembree_1955.pdf
Colby, B. R. 1957.
Relationship of unmeasured discharge to mean velocity.
Transactions, American Geophysical Union, 38(5), Oct., 708-717.
https://ponce.sdsu.edu/colby1957agu.pdf
Colby, B. R. 1964.
Discharge of sands and mean velocity relations in sand-bed streams.
U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 462-A, Washington, D.C.
https://ponce.sdsu.edu/usgsprofessionalpaper462A_colby1964.pdf
Ponce, V. M. 2014.
Engineering Hydrology: Principles and Practices. https://ponce.sdsu.edu/enghydro/index.html
|
| 240311 |