Satellite image of the neighboring Coipasa and Uyuni salt flats.
|
|
| |
|
The connection between the Coipasa and Uyuni Salt Flats, Bolivia
Victor M. Ponce, Luis G. Ariza, y
Rodolfo J. Vera Quispe
19 June 2017
|
|
The salt flats of Coipasa and Uyuni are two large natural
accumulations of salt (salt lakes) located within the endorheic hydrographic basin
of the Peruvian-Bolivian altiplano. The Coipasa salt flats,
in the department of Oruro (Bolivia) has an area of 2 239 km2 and an average altitude of 3,657 meters. However, it should be noted that a
very small fraction of the Coipasa salt flats lie in the
neighboring country of Chile. The Uyuni salt flats, in the
department of Potosí, has an area of 10 085 km2 and an
average altitude of 3,653 above m.s.l. (Chua and Ponce, 2010).
This article documents the existence of a hydraulic connection between the two salt flats.
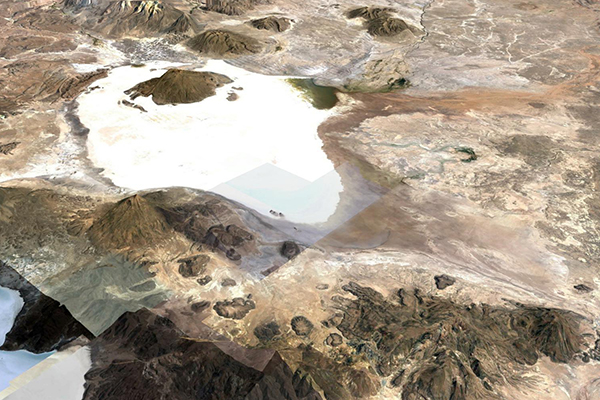
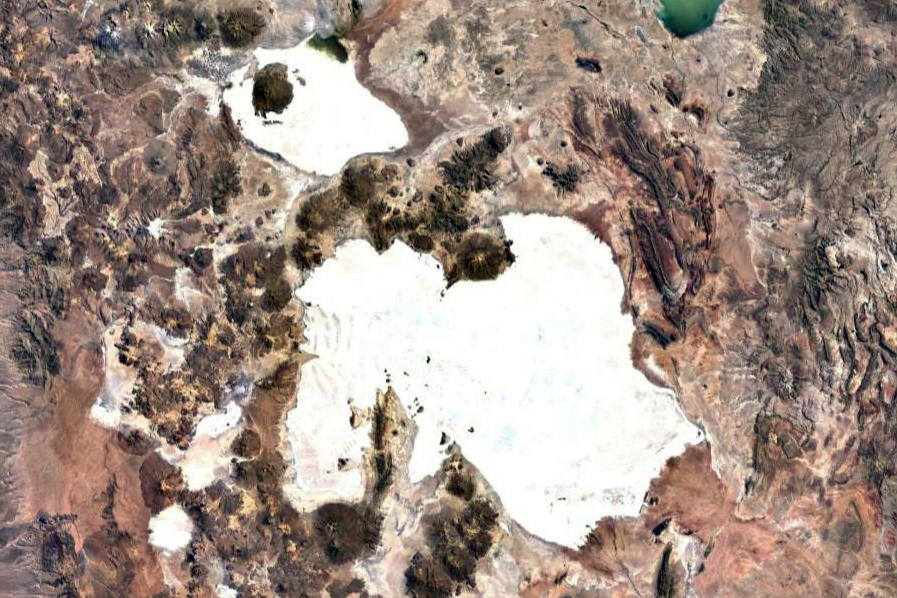
Figure 1 shows an aerial perspective of the Coipasa salt flats.
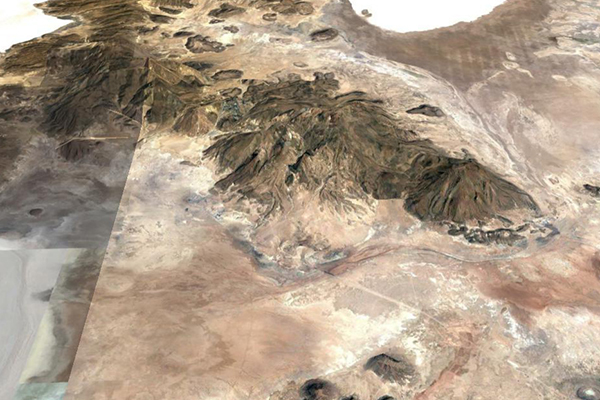
Figure 2 shows the old (remnant) trace of the stream or channel
that connects the Coipasa salt flats (near the upper right corner)
with the Uyuni salt flats (lower left corner). This stream borders
the Tunupa volcano in the vicinity of Cacota, Laguna Cruz and
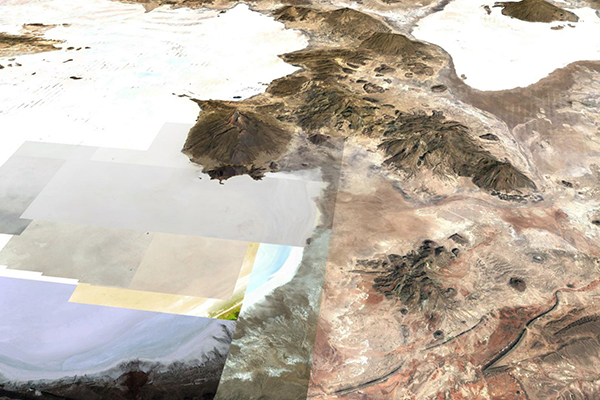
Castillona, eventually leading to the Uyuni salt lake, as shown in Fig. 3.
|
Fig. 1 The Coipasa salt flats.
|
|
|
Fig. 2 Connection between the Coipasa and Uyuni salt flats,
around the Tunupa volcano.
|
|
|
Fig. 3 Aerial perspective of the
Coipasa dn Uyuni salt flats, with the Tunupa volcano in the middle.
|
|
Based on the information examined, it can be concluded that
there is a connection between the two salt flats. The difference
in elevation is estimated at 5 m, with the flow originating in the
salt flats of Coipasa and ending in the salt flats of Uyuni. Therefore,
the latter is the terminus of the drainage of the Peruvian-Bolivian
altiplano basin, which contains, upstream, Lake Titicaca, and
downstream, the salt flats of Coipasa and Uyuni, among
others (Chua and Ponce, 2010).
A more detailed analysis may be obtained by applying a
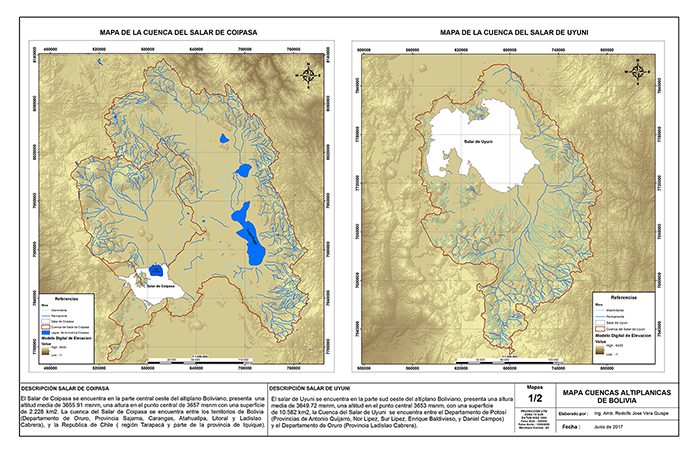
geographic information system (GIS) to the satellite images of the Coipasa and Uyuni drainages. Figure 4 shows the contiguous watersheds of both salt flats.
| [Click on image to display] |
|
Fig. 4 The hydrographic basins of the Coipasa and Uyuni salt flats.
|
|
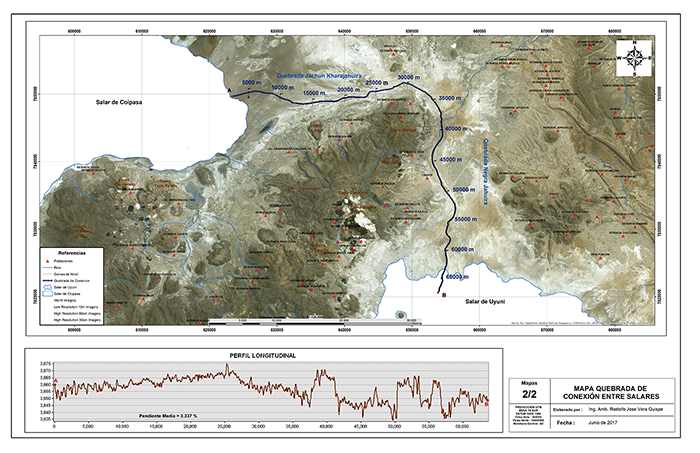
Figure 5 shows the hydraulic connection between the Coipasa and Uyuni salt flats.
The effective difference in elevation,
with the Coipasa salt flats upstream and the Uyuni salt flats downstream,
is shown to be about 10 m. It is inferred that during extraordinary floods,
the water of Coipasa lake has flowed towards
Uyuni lake. Therefore, it is confirmed that Uyuni
is the terminus of the drainage of the Peruvian-Bolivian
altiplano basin.
| [Click on image to display] |
Fig. 5 Hydraulic connection between the Coipasa salt flats,
upstream, and the Uyuni salt flats, downstream.
|
|
Chua, J. H., and V. M. Ponce. 2010.
Drainage basin of the Altiplano, South America.
http://ponce.sdsu.edu/chua/altiplano_drainage_basin.html
15 October 2010.
|